Passive immunity often provides effective protection but this protection disappears with time usually within a few weeks or months. Passive immunity is protection by products produced by an animal or human and transferred to another human usually by injection.
 Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It
Acquired Immunity What Is It And How Do You Get It
Immunity produced by the transfer to one person of antibodies that were produced by another person.

Natural passive immunity definition. Antibodies are transferred from one person to another through natural means such as in prenatal and postnatal relationships between mother and child. An individual may be naturally immune to certain pathological conditions or may acquire immunity through either active or passive means. For example antibodies passed from the mother to the baby before birth confer passive immunity to the baby for the.
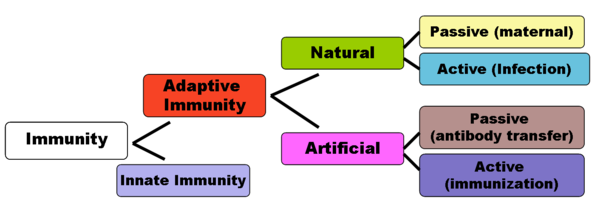
Natural immunity occurs through contact with a disease causing agent when the contact was not deliberate where as artificial immunity develops only through deliberate actions of exposure. Immunity possessed by a group as a species or race that is present in an individual at birth prior to exposure to a pathogen or antigen and that includes components as intact skin salivary enzymes neutrophils natural killer cells and complement which provide an initial response against infection called also natural immunity. When it happens to enough people and each case is different so we cant put a clear number on it especially given so many cross immunities.
If the virus doesnt kill its host it can hop to others through all the usual means. Sensitized T cells can also confer passive immunity. Naturally acquired passive immunity occurs during pregnancy in which certain antibodies are passed from the maternal blood into the fetal bloodstream in the form of IgG.
Natural immunity is a genetic characteristic of an individual and is due to the particular species and race to which one belongs to ones sex and to ones individual ability to produce immune bodies. Protection from passive immunity diminishes in a relatively short time usually a few weeks or months. Some antibodies can cross the.
The more this occurs the less it spreads. And also human breast milk that comprises the IgA. Breastfeeding provides a baby with natural passive immunity.
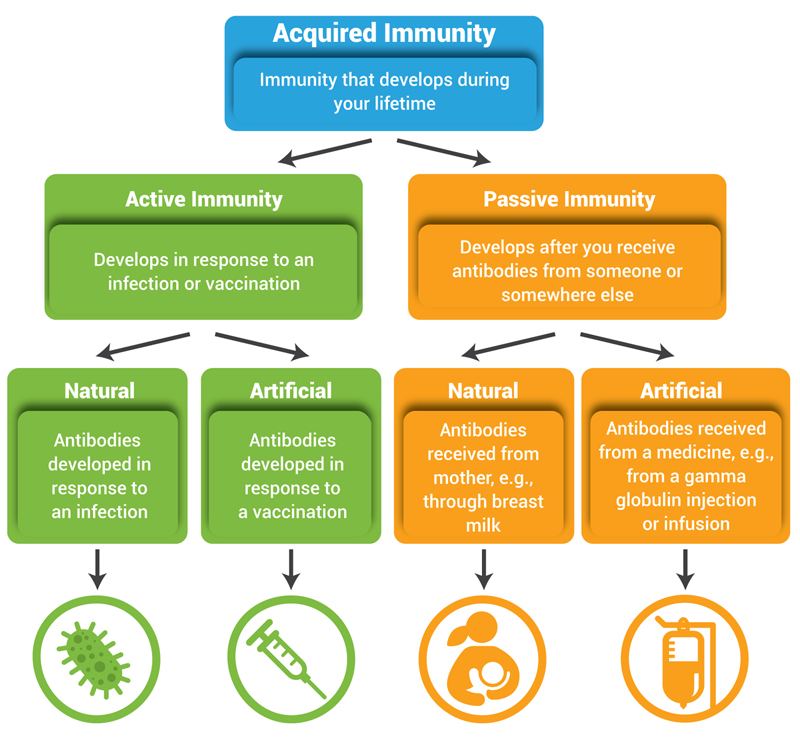
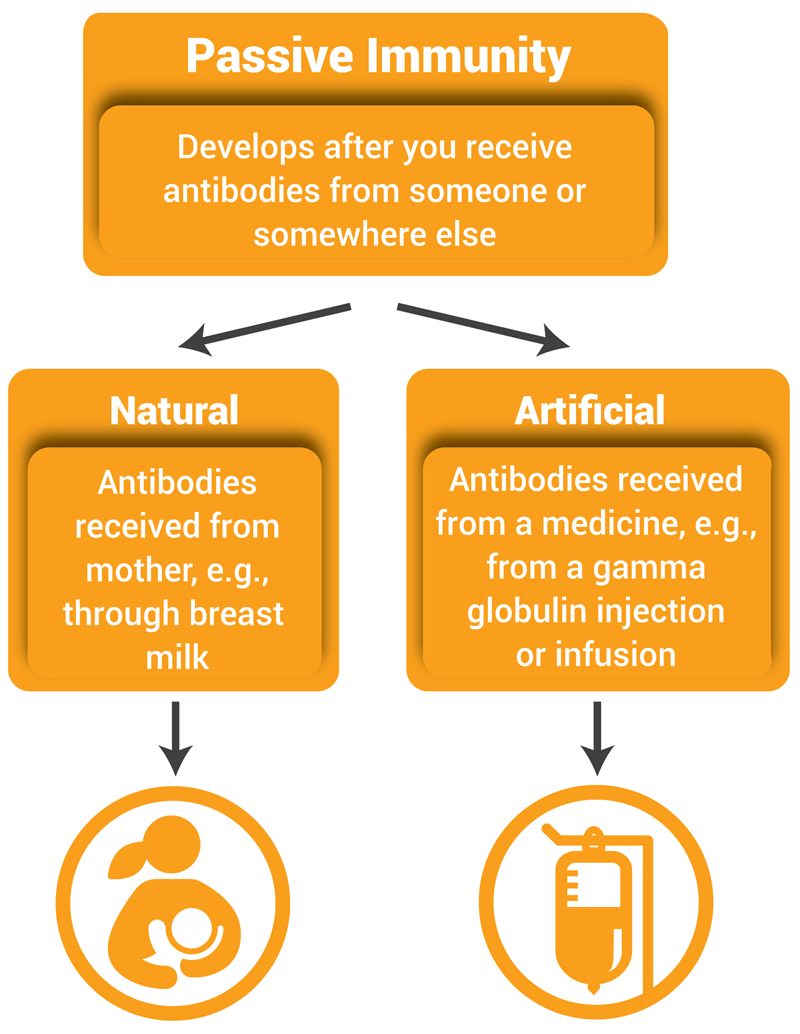
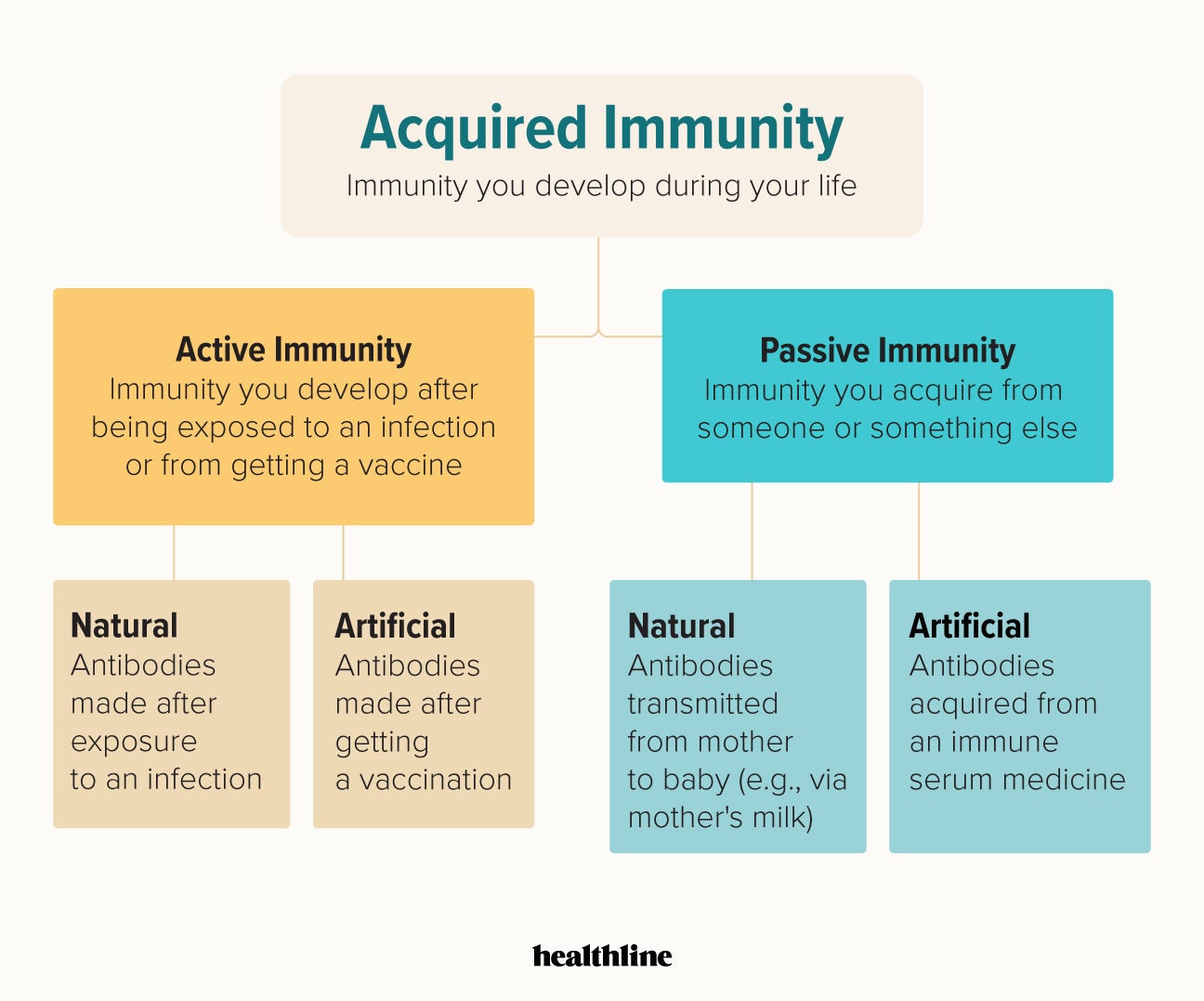
Passive immunity - an impermanent form of acquired immunity in which antibodies against a disease are acquired naturally as through the placenta to an unborn child or artificially as by injection of antiserum. Both natural and artificial immunity can be further subdivided depending on the amount of time the. Collins Dictionary of Medicine Robert M.
Protection against disease in the form of antibodies substances in the blood that fight disease that come from someone else for example from the mothers milk Definition of passive immunity from the Cambridge Academic Content Dictionary Cambridge University Press Examples of passive immunity. Immunity especially to specific infections resulting from the acquisition of ANTIBODIES either by injection or by transfer through the PLACENTA or ingestion in the breast milk. Artificial immunity can be active or passive.
For example during pregnancy the placental transfer of IgG from a mother to fetus takes place that generally lasts 4 to 6 months after birth. Passive immunity develops after you receive antibodies from someone or somewhere else. When you get a virus and fight it off your immune system encodes that information in a way that builds immunity to it.
Immunity that is naturally existing Natural immunity does not require prior sensitization to an antigen. Passive immunity can occur naturally such as when an infant receives a mothers antibodies through the placenta or breast milk or artificially such as when a person receives antibodies in the form of an injection gamma globulin injection. Passive immunity is a state where antibodies are given to a person to prevent or fight against disease or to treat disease after the body is exposed to an antigen.
Immunity to a disease is achieved through the presence of antibodies to that disease in a persons system. In passive def immunity antibodies def made in another person or animal enter the body and the immunity is short-lived. Antibodies are proteins produced by the body to neutralize or destroy toxins or disease-carrying organisms.
Only lasts a short period of time. With active def immunity antigens def enter the body and the body responds by making its own antibodies and B-memory cells def. This type of immunity is short-lived because it doesnt cause your immune system to recognize the pathogen in.
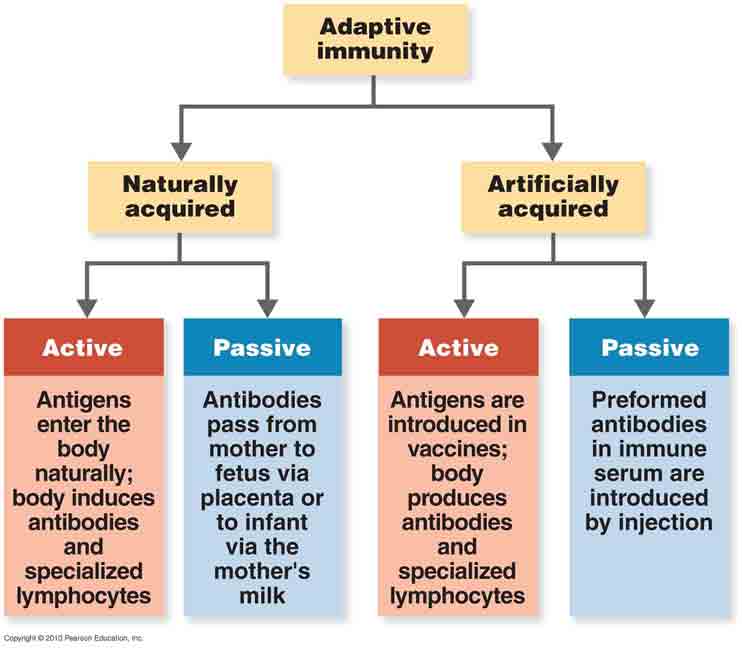 What Is The Difference Between The Four Types Of Human Immunity Socratic
What Is The Difference Between The Four Types Of Human Immunity Socratic
 Difference Between Active And Passive Immunity In Tabular Form
Difference Between Active And Passive Immunity In Tabular Form
 Passive And Active Immunity Flashcards Quizlet
Passive And Active Immunity Flashcards Quizlet
Difference Between Active And Passive Immunity Definition Features Types Similarities
 Active Vs Passive Immunity Differences And Definition Technology Networks
Active Vs Passive Immunity Differences And Definition Technology Networks