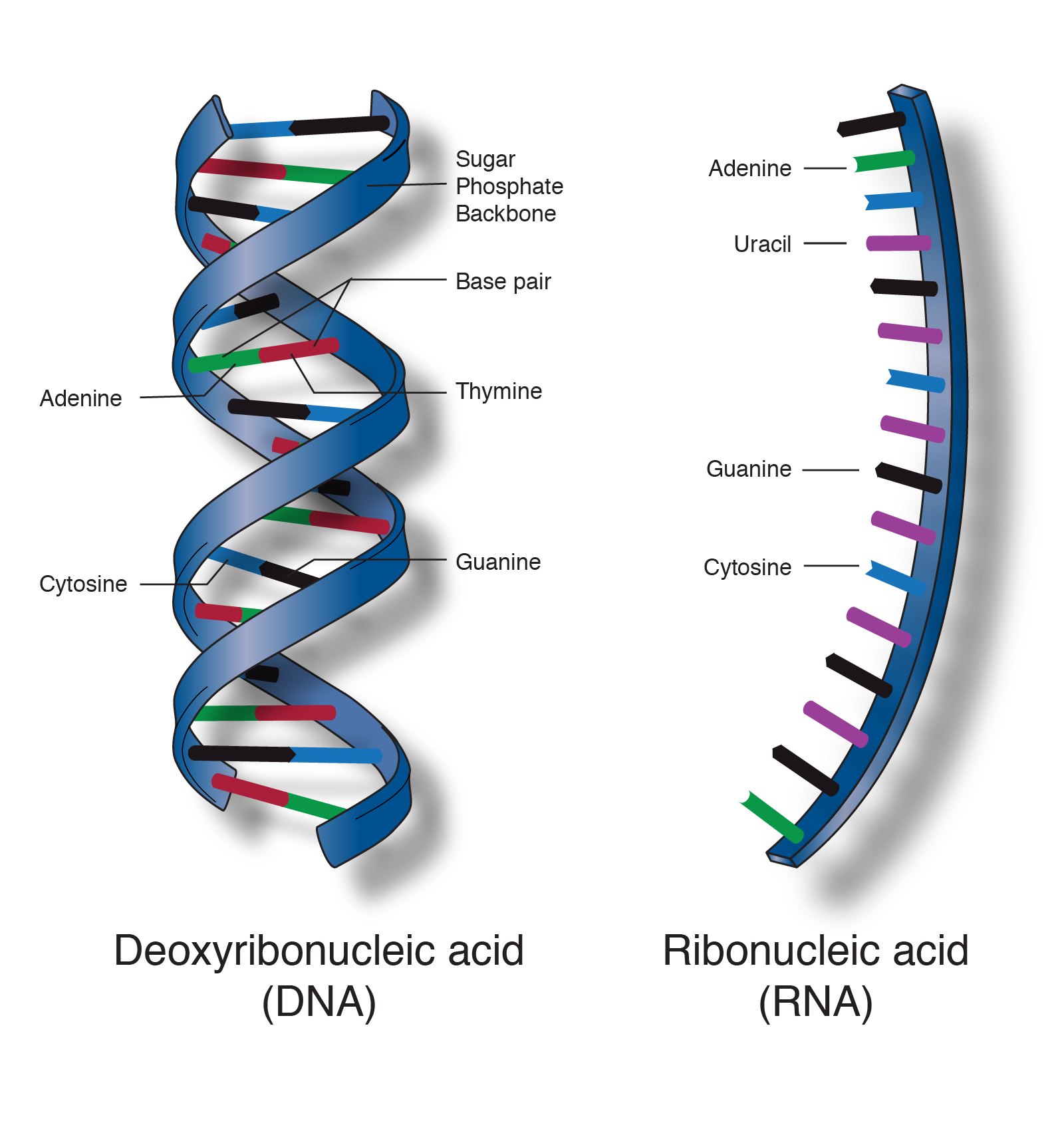
The principal nucleic acids DNA and RNA are the carriers of hereditary information and control the synthesis of proteins. American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition.
DNA and RNA are responsible for the inheritance and transmission of specific.

Nucleic acid biology definition. Any of various complex organic acids such as DNA or RNA that are composed of nucleotide chains Examples of nucleic acid in a Sentence Recent Examples on the Web Every day millions of Americans immune systems are reprogrammed by sophisticated strands of frozen nucleic acid. Denaturing nucleic acids. The complex of nucleic acids in your body is like a construction team where some members give instructions and others put.
Thus each sugar and phosphoric acid forms bonds with two. The Nucleic Acid Is A Large Molecule Which Is Very Important For Life It Has A Genetic Information Code. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA are two major types of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids are a long chain polymers of nucleotides which are joined together by means of phosphodiester linkages. Figure 2141 - The hyperchromic effect Wikipedia. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells.
Types Of Nucleic Acid-. Nucleic acidDefinition Function StructureTypesnucleic acid class 11 biology. Nitrogenous Base A T G C U.
Nucleic acid definition any of a group of long linear macromolecules either DNA or various types of RNA that carry genetic information directing all cellular functions. Biological Functions Of Lipids-Membranes. Nucleic AcidDefinition Nucleic acidis the chemical name for the molecules RNAand DNA.
Nucleic acids are small biological molecules that are essential to all known forms of life. Any of a class of large molecules that are polymers of nucleotides and are found in all living organisms and viruses. Definition of nucleic acid.
Nucleic acid in Biology topic. Like proteins nucleic acids can be denatured. The different kinds of nucleic acids collectively work together to create encode and store genetic information and make proteins based on that information.
The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Start studying Biology Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are long-chain polymeric molecules the monomer the repeating unit is known as the nucleotides and hence sometimes nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides.
Pentose Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Forces holding duplexes together include hydrogen bonds between the bases of each strand that like the hydrogen bonds in proteins can be broken with heat or urea. In phosphodiester bonds one phosphoric acid molecule forms bonds with the 3 carbon of one pentose molecule as well as with the 5 carbon of a second pentose molecule.
From Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English nucleic acid nucleic acid njuːˌkliːɪk ˈæsəd -ˌkleɪ- nuː- noun countable uncountable HBM one of the two acids DNA and RNA that exist in the cells of all living things Examples from the Corpus nucleic acid The test only confirms that the organisms nucleic acid is present. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. They play an especially important role in directing protein synthesis.
Asslamulalikum I am Muhammad Jamal Javed Welcome to our youtube channel Mr DAE ENGINEER.